Evolutionary body
At Daihatsu, our goal is to create cars that can be used with peace of mind and with comfort in a range of everyday scenarios, such as for commuting, carrying passengers, and work; we strive to deliver cars that are both cheap to maintain and friendly to the environment.
New DNGA platform
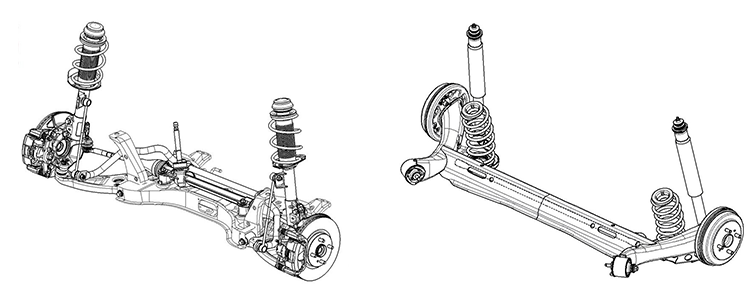 Suspension
Suspension
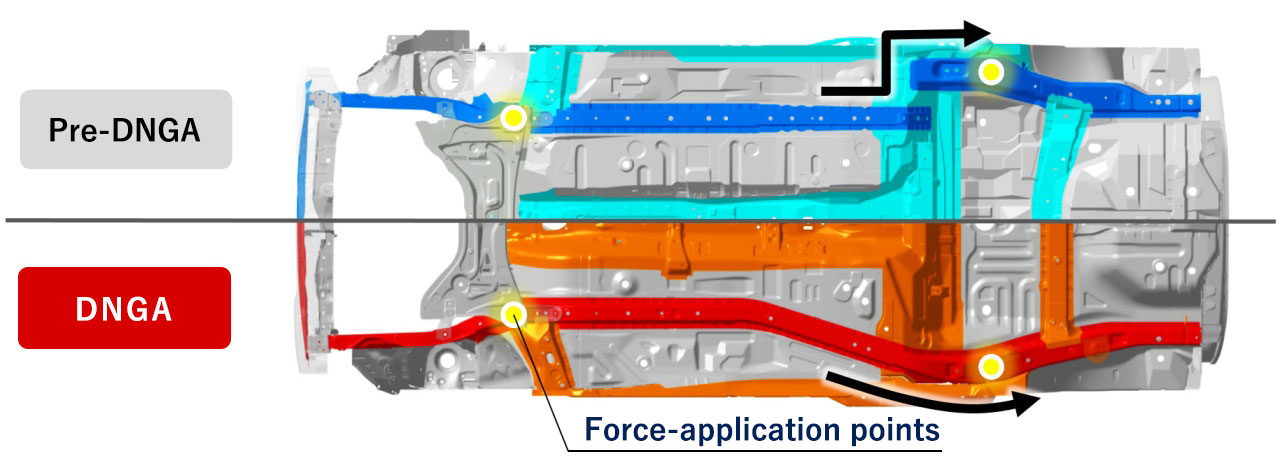 Underbody
Underbody
In order to realize class-beating stability and comfort, our suspension geometry features a new design with optimized bush properties, spring numbers, and shock-absorbing characteristics.
In addition, by linking force-application points at the front and rear of the vehicle, we have smoothed the transmission of force through the frame.
Lightweight, high-rigidity body
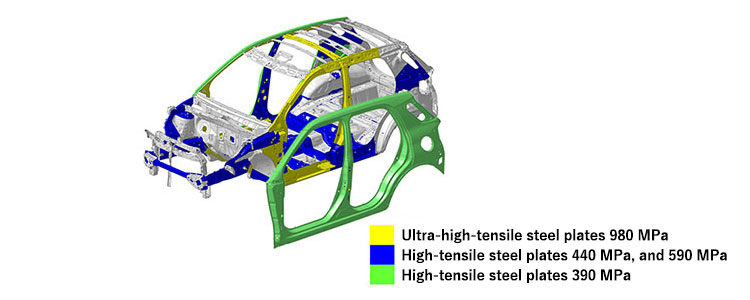 Rocky D monocoque
Rocky D monocoque
The use of thicker, high-tensile plates for the side-door outer panels enables them to be used as strength members; consequently, since strength-member reinforcements no longer have to be used, this results in a lightweight, high-rigidity body.
Adopted Light-weight Resin instead of Steel Plate for External Parts
 Wake
Wake
 Sections using resin parts
Sections using resin parts
Daihatsu is making vehicles lightweight by increasing the use of resin for body parts. Based on tests of resin parts in various temperature conditions to investigate distortion conditions, Daihatsu has developed a processing method and material selection process reflecting the requirements for optimization of each part.
High-tensile materials, thinner outer panels and partitions
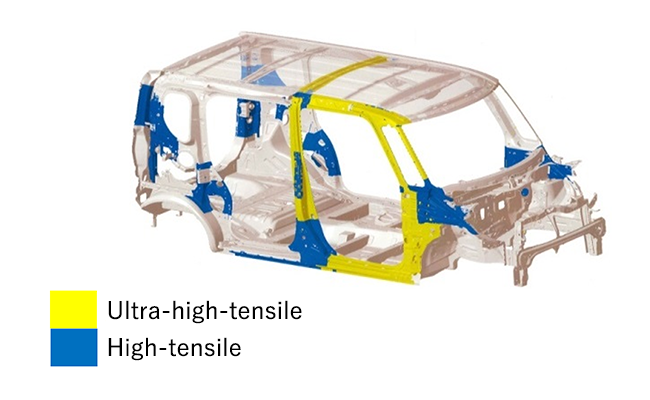 Tanto: high-tensile materials
Tanto: high-tensile materials
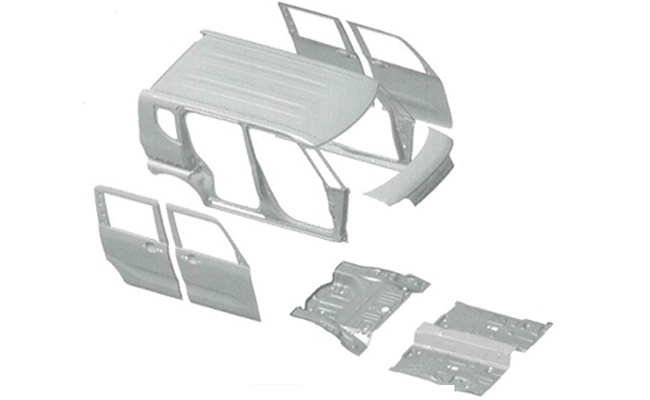 Tanto: thinner outer panels and partitions
Tanto: thinner outer panels and partitions
By selectively using high-tensile materials and thinner outer panels and partitions, we have succeeded in reducing the weight of the body.
Lightweight resin fuel tank
 Copen: resin fuel tank
Copen: resin fuel tank
In order to reduce weight, our fuel tank is made of resin with a uniform wall thickness; for improved rigidity and shock absorption, we have used pseudo-cylindrical concave polyhedral (PCCP) patterning.
Secure and comfortable driving position
Easy-to-drive pedal and steering wheel layouts
 Move: steering wheel position
Move: steering wheel position
 Move: pedal layout
Move: pedal layout
Reducing the distance between the driver and the steering wheel has enabled us to realize a superior driving position.
We have also increased the vertical distance between the accelerator and brake pedals to help prevent them from being pressed at the same time.
Quiet cabin space
Wind noise generated while driving and other external noises have been reduced.
 Tanto: interior space
Tanto: interior space
Incorporating aerodynamic considerations into our design development, modifying height-differences at the front and sides of the vehicle, and reviewing mirror shapes have allowed us to limit wind disturbance and so reduce wind noise; we have also minimized the number of drainage holes and other openings in the body to block acoustic pathways, which are a source of unwanted noise. Improved positioning of sound-absorbing materials and increased steering rigidity result in significant reductions in both noise and vibrations as well.
Outstanding driving performance
D-Frame framework structure guarantees rigidity appropriate to a sports car
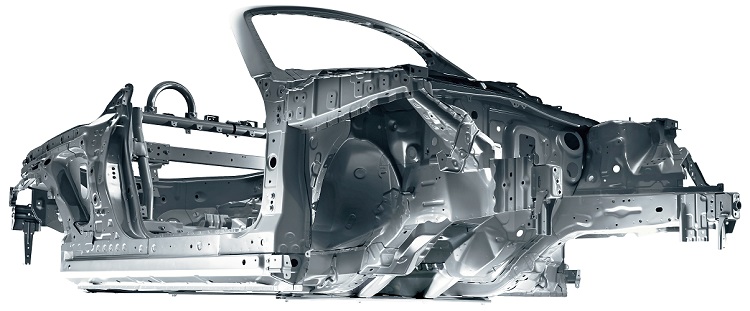 Copen: D-Frame framework structure
Copen: D-Frame framework structure
D-Frame is a framework structure in which the entire body—including front, sides, rear, and floor—uses a seamless construction, with reinforced underfloor tunnel parts and cross members; the structure realizes significantly enhanced torsional rigidity and vertical flexural rigidity. Since rigidity appropriate to a sports car is generated by the framework alone, the D-Frame delivers outstanding steering stability.
*Note: Above is the proto-type photo so the specifications may differ from the current sales model.