Management of Environmental Load Substances in Production Activities / Management of Water Resources / Chemical Substances and Risk Management
-
Fundamental Approach / Environmental Management Structure / Daihatsu Group Initiatives
-
Management of Environmental Load Substances in Production Activities / Management of Water Resources / Chemical Substances and Risk Management
-
Environment Month Events / Environmental Education
-
Daihatsu Environmental Communication System / Environmental Communication with Local Communities
Prevention of Air Pollution
Daihatsu properly manages and reduces environmental load substances in our production activities in accordance with the Environmental Action Plan and all relevant laws and regulations.
The Air Pollution Control Act sets out regulatory exhaust gas values for every type of facility. In order to prevent exhaust gases from our plants from causing air pollution, Daihatsu regularly measures and monitors exhaust gases generated by boilers and heaters, and ensures that both SOx and NOx concentrations remain significantly below regulatory values.
With regard to atmospheric emissions of VOCs*, which are a cause of air pollution, we have carried out a variety of activities in accordance with the Environmental Action Plan aimed at reducing emissions volumes in the painting process, which accounts for the majority of VOC emissions. These include automating painting processes to improve coating efficiency, robotization, the use of electrostatic processes, and the recovery of thinners used to clean equipment. To drastically reduce VOC emissions, we are switching middle and top paint coats to water soluble paint at the Kyoto (Oyamazaki) Plant and the Daihatsu Motor Kyushu Co., Ltd. Oita (Nakatsu) Plant. We are also addressing chemical substances in production activities by complying with all relevant laws and regulations to ensure that we do not use banned substances.
* VOC: Volatile Organic Compounds. Common VOCs include toluene, xylene, and other substances found in paints.
Regulation and Standards
| Head (Ikeda) Plant |
|
|---|---|
| Kyoto (Oyamazaki) Plant |
|
| Shiga (Ryuoh) Plant |
|
| Daihatsu Motor Kyushu Co., Ltd. Oita (Nakatsu) Plant |
|
Environmental Measurement Certification Site (Registered with Osaka Prefecture)
Osaka Prefecture registers Daihatsu as an environmental measurement certification site, which can accurately measure concentration of pollutants in water, air, and soil and publicly verify the results. This role is performed by the internal department responsible for environment measurements. They conduct sampling and chemical analysis and work in collaboration with each business site to prevent environmental abnormalities so that the various gases emitted and harmful substances in waste water generated during Daihatsu’s business activities* do not exceed statutory standards. In addition, qualified personnel take measurements in work environments to protect the health of employees.
* Main business sites: Ikeda (Osaka Prefecture), Shiga, Kyoto, Tada (Hyogo Prefecture), Daihatsu Kyushu Co., Ltd. Oita (Nakatsu) Plant
Business Flow
Management of Water Resources
Dealing with water resources has become an extremely important issue for companies as a result of tight supplies of water due to the rising global population and climate change as well as stricter regulation in conjunction with the deterioration of water quality in rivers and other water sources. To minimize the effect on the water environment from our business activities, the Daihatsu Group is taking various measures to reduce water usage and recirculate and reuse water by purifying waste water.
Water Usage Reduction Initiatives
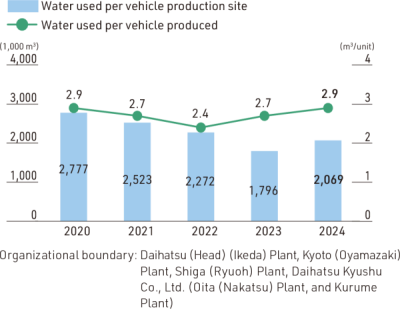
Water use is essential for automobile manufacturing in the painting and other processes. The Daihatsu Group is implementing water usage reduction measures at our vehicle production sites with a focus on painting processes. In the pretreatment and electrodeposition cleaning processes, we strive to ensure that water used in the cleaning process is effectively reused, thereby reducing water usage. In addition, we have developed and introduced an innovative cardboard filter-type dry booth for the painting process, and are working to reduce the amount of water used by replacing the conventional paint collection method that uses a water shower (gas-liquid mixture) with a dry filter*. As a result of these efforts, the amount of water used per vehicle, which was 6 m3 in 1995, has now been reduced to less than half. Going forward, we will pursue SSC (simple, slim, and compact) vehicle manufacturing even more and work to minimize water usage, thereby contributing to the conservation of water resources.
* This technology won the Machine Promotion Award in December 2022.
Water Used Per Vehicle Production Site / Water Used Per Vehicle Produced in Japan
Purification and Reuse of Waste Water
At the Shiga (Ryuoh) Plant, Daihatsu has built the Aqua Center—a large-scale plant waste water purification facility—to guarantee the quality of water discharged into Lake Biwa. The Aqua Center purifies plant waste water to an almost drinkable level before discharging it into the lake. The Shiga (Ryuoh) Plant reuses water purified at the plant’s waste water processing facilities for its wet dust collectors. Our production bases in Indonesia and Malaysia take the greatest care to ensure that their plant waste water has no impact on downstream drinking water collection sites.
 Shiga (Ryuoh) Plant Aqua Center No. 3
Shiga (Ryuoh) Plant Aqua Center No. 3
 Waste water after purified at the Aqua Center
Waste water after purified at the Aqua Center
Standards for Waste Water
Standards for plant waste water vary according to where we discharge the waste water, such as public rivers or sewers, and the local governments of the prefectures in which Daihatsu plants operate. At all plants, the Daihatsu Group sets voluntary standards that exceed those set by the national and local governments and discharges waste water only after it is purified to a sufficiently clean level.
Regulation and Standards
| Head (Ikeda) Plant |
|
|---|---|
| Kyoto (Oyamazaki) Plant |
|
| Shiga (Ryuoh) Plant |
|
Chemical Substances
Daihatsu actively manages the chemical substances in the materials that we use in automobiles and other products as well as facilities. We manage chemical substances in purchased parts and materials used in production processes and facilities, create a chemical substance database, and perform entry management to ensure compliance with the many applicable laws and regulations.
Management of the chemical substances contained in products is conducted using IMDS1, the global automobile industry standard, and is compliant with global regulations on chemical substances. The chemical substances used at facilities are monitored using a system called PRTR-WORLD, which quantitatively tracks chemical substance emissions and movements, in addition to properly reporting this information to the authorities.
In order to ensure that our parts and materials suppliers also understand the importance of chemical substance management, we use self-diagnostic sheets created by an auto industry organization to monitor management levels at suppliers and pursue improvements thereof.
We also work with the affiliated companies that produce Daihatsu products in Japan and around the world to regularly share information on chemical substance management and provide support when necessary to enable them to perform chemical substance management at the same level as Daihatsu itself.
1. IMDS: International Material Data System, a material data system for the automobile industry
| Applicable Laws PRTR Law2 |
|
|---|---|
| Applicable Laws Chemical Substances Control Law4 |
|
2. PRTR Law: Act on the Assessment of Releases of Specified Chemical Substances in the Environment and the Promotion of Management Improvement
3. DEM: Daihatsu Environmental Manual
4. Chemical Substances Control Law: Act on the Regulation of Manufacture and Evaluation of Chemical Substances
Risk Management Relating to Environmental Laws and Regulations
Daihatsu has established and operates environmental management systems in accordance with ISO 14001 in all internal organizations to ensure compliance with the enactment and revision of all environmental laws, regulations, ordinances, and so on, particularly those relating to production activities. For example, we have incorporated into work systems prior investigation of environmental conservation and energy reduction when we introduce equipment (in the planning stage), confirming inspections at the time of introduction (before operation), and regular internal audits (during operation), and we also conduct PDCA of environmental management systems. We began operating ISO 14001 at the Kyoto (Oyamazaki) Plant in 1998 and have acquired and maintained certification for all internal organizations as discussed above since 2017.
As a result of these efforts, we had no environmental accidents, abnormalities, complaints, or legal violations in fiscal 2025. We commit ourselves to continuing and enhancing these measures in the future.
The Daihatsu Group has obtained ISO 14001 certification at all business sites and strives to prevent all environmental abnormalities, complaints, and legal violations through day-to-day management in accordance with environmental management systems.