End-of-life Vehicle Recycling Initiatives
Compliance with the Act on Recycling of End-of-Life Automobiles
The Act on Recycling of End-of-Life Automobiles came into force in January 2005. Since then, automobile manufacturers have been responsible for recovering and recycling shredder dust, airbags, and fluorocarbons1 generated by end-of-life vehicles. Daihatsu plays an active role in building systems that facilitate the implementation of the Act and works together with affiliated businesses both to make recycling more commonplace and improve the rate of recycling. In addition, we engage in the development of vehicles that can be recycled with minimal load on the environment.
1. Fluorocarbons are destroyed
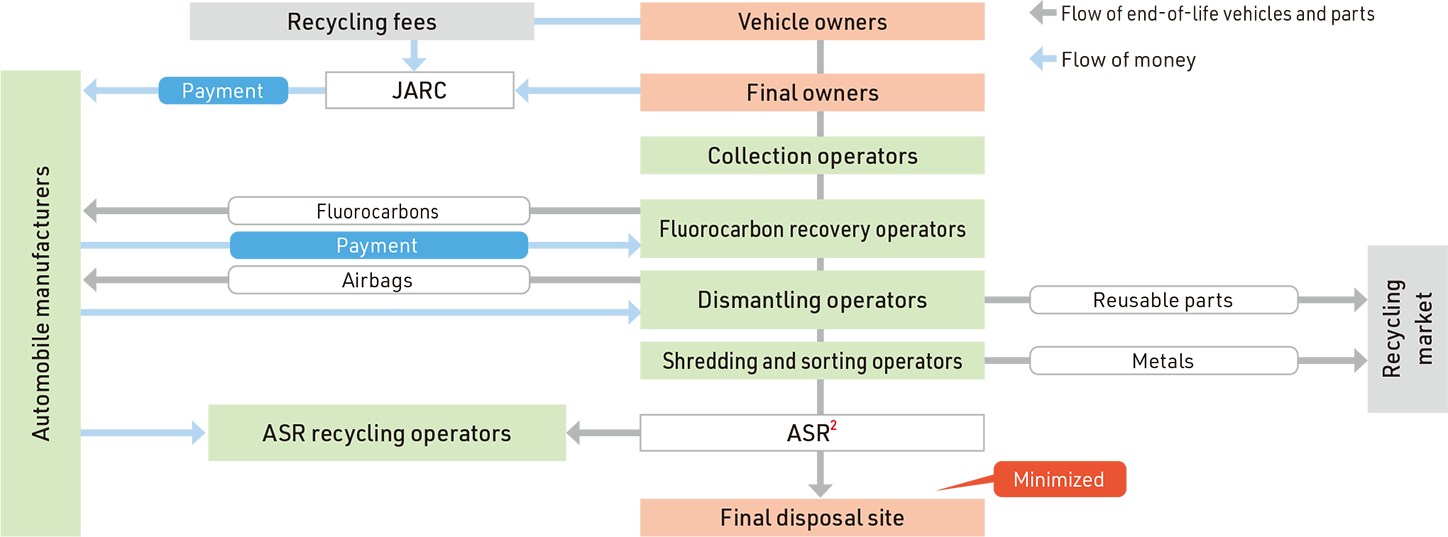
Overview of the Act on Recycling of End-of-life Automobiles
2. ASR: Automobile shredder residue
Implementing Recovery and Recycling of Three Items3
Daihatsu recovers and recycles airbags and fluorocarbons (fluorocarbons are destroyed) in an efficient manner through the Japan Auto Recycling Partnership—an organization established together with other automobile manufacturers to recover and recycle such items. We also recover and recycle shredder dust through Toyotsu Recycle Corporation’s ASR Recycling Business Department, which was jointly established by Daihatsu, Toyota Motor Corporation, Honda Motor Co., Ltd., and Hino Motors, Ltd.
3. Airbags, fluorocarbons, and shredder dust
Examples of Initiatives
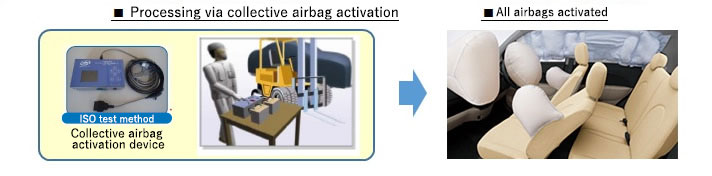
Airbag Initiatives
Daihatsu equips all of its vehicles with airbag collective activation connectors, which enable all airbags in a vehicle to be simply activated without having to be removed. We also provide registered vehicle dismantling companies with instructions on how to dismantle and activate airbags in a simple and safe manner via our online Proper Airbag Processing Manual.
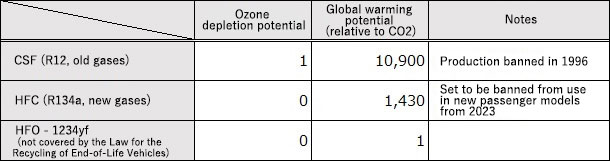
Fluorocarbon Initiatives
With regard to fluorocarbons used as refrigerants in air conditioners, Daihatsu completely eliminated the use of specified chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) and switched to the use of alternative hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs) in 1994. In addition, we adopted HF0-1234yf, an alternative fluorocarbon, for all passenger vehicles.
■Characteristics of fluorocarbons used in vehicle air-conditioning systems
Shredder Dust Initiatives
Daihatsu prioritizes the use of easy-to-recycle thermoplastic resins such as polypropylene and polyethylene and pursues designs that make dismantling and disassembling of vehicles easier. We also use dismantling enhancement marks to clearly indicate how larger components can be easily dismantled. In order to promote the recycling of whole dismantled vehicles—whereby dismantled vehicles have their copper parts removed and are then directly recycled in electric furnaces—we provide instructions on how to remove copper parts (such as wiring harnesses and motors) to consortiums that carry out the recycling of whole dismantled vehicles.
Releasing information on recycling of end-of-life vehicles and information to processing companies
(1) In compliance with the requirements of the Law for the Recycling of End-of-Life Vehicles, Daihatsu releases information of recycling fees for different models and implementation status of recycling. In this way, we strive both to realize efficient recycling activities, and to improve its recycling rates.
Daihatsu provides information to automobile recyclers regarding collection fees, transportation fees, collection standards, and collection locations. Additionally, we provide work procedure manuals to ensure the safe processing of drive batteries, CNG (compressed natural gas) vehicle gas cylinders.
Maintenance and management initiatives
- To ensure that recyclers are processing its end-of-life vehicles in compliance with the Law for the Recycling of End-of-Life Vehicles, Daihatsu accompanies contractors to carry out audits of these recyclers. The audits entail on-site confirmations of processing work and facilities for ASR, airbags, and fluorocarbons; at the same time, they verify processing volumes and public commitments.
- Local governments are responsible for managing processing facilities, and Daihatsu works together with the Japan Auto Recycling Partnership to provide lecturers to train the local government employees responsible.
Initiatives for the Future
Going forward, Daihatsu will continue to promote the stable processing of end-of-life vehicles in compliance with the Law for the Recycling of End-of-Life Vehicles. We also work together with other automobile manufacturers and affiliated businesses to further develop recycling technologies, and to establish schemes to cater to the future spread of electrified vehicles.
Key Initiatives
1. Expanding the scope of materials that can be recycled through developments in ASR sorting technologies
2. Promoting activities aimed at the proper processing of batteries from hybrid and other electrified vehicles, and promoting the microgrid concept
3. Steadily switching to the use of fluorocarbons (conform the Montreal Protocol on Substances that Deplete the Ozone Layer, and the Act on Rational Use and Proper Management of Fluorocarbons)
Examples of Concrete Initiatives
Initiatives for Difficult-to-process Parts
Some resin outer panel parts contain glass fiber or carbon fiber for lighter weight, and this makes them difficult to recycle and process. Daihatsu collects these difficult-to-process parts from its sales companies, before independently processing them.
 Resin outer panel parts (rear doors, etc.)
Resin outer panel parts (rear doors, etc.)
 Limited-edition Copen with CFRP roof
Limited-edition Copen with CFRP roof
Use of Recycled Plastic
In September 2024, the Japan Automobile Manufacturers Association, Inc. (of which Daihatsu is a member) formulated and released its “2050 Long-term Vision and Medium- to Long-term Roadmap (including self-imposed target values)” that aims to promote the supply and use of recycled materials.
Daihatsu plans to expand usage of a wider range of recycled plastics for the purpose of steadily achieving the specific targets indicated for 2030, 2035, and 2040 on the road to 2050.
Recycling Repaired and Replaced Bumpers
- Daihatsu collects repaired and replaced bumpers from dealers, then crushes, melts, and pelletizes them. These pellets are then reused to make parts for our vehicles, such as seat undertrays and engine undercovers.
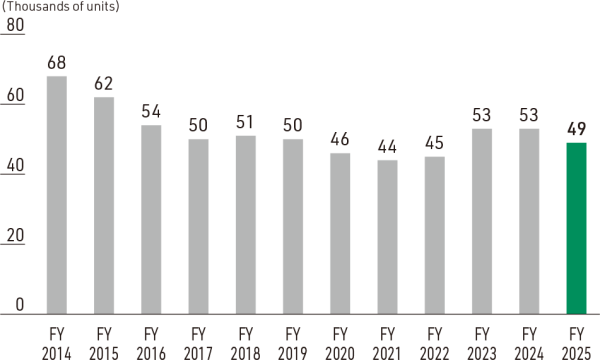
■Number of repaired and replaced bumpers collected