Initiatives for Production
-
Fundamental Approach and Targets
-
Initiatives for Products
-
Initiatives for Production
-
Initiatives for Non-production
-
Initiatives for Logistics
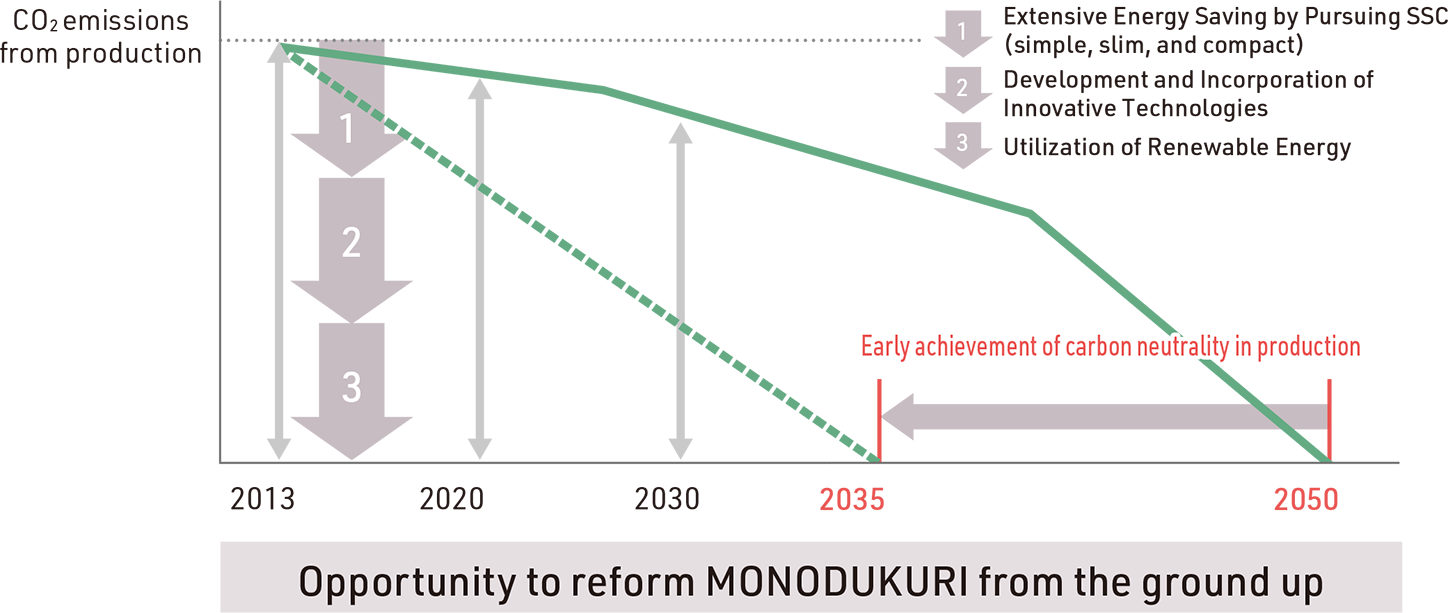
Pursuing Carbon Neutrality in Production by 2035
As a member of the Toyota Group, to make further contributions to the development of a low-carbon society, which is a global issue, the Daihatsu Group greatly moved up the 2050 target for achieving carbon neutrality in production, setting a new target of 2035. We now seek to achieve carbon neutrality in production by 2035 by reducing CO2 emissions in the production processes* of Daihatsu Motor and our subsidiaries. To achieve this lofty target, we established the Production & Logistics Carbon Neutral Promotion Department as a specialized organization in January 2022 and began taking action in three areas: extensive energy saving by pursuing SSC (simple, slim, and compact), development and incorporation of innovative technologies, and utilization of renewable energy. The Kyoto (Oyamazaki) Plant was upgraded in October 2022 and designated as a model plant. We then drew on this accumulated technology and expertise in 2024 when we set up the second production line at the Karawang Vehicle Plant in Karawang, Indonesia. We will continue rolling out this technology and expertise in Japan and overseas as we promote measures for achieving carbon neutrality in production throughout the Daihatsu Group.
* Daihatsu Motor’s production sites and production subsidiaries with over 50% stake
Refinement at the Kyoto (Oyamazaki) Plant with an Eye toward Carbon Neutrality
The Kyoto (Oyamazaki) Plant has been producing mainly compact cars including Toyota vehicles, the Charade, and the Terios for approximately 50 years since operations began in April 1973. Daihatsu refined the plant in September 2018 and upgraded it in October 2022 to maintain and enhance competitiveness in environmental performance, quality, and production. Today, the plant is pursuing production based on SSC (simple, slim, and compact), Daihatsu’s MONODUKURI concept, and implementing extensive energy saving with an eye toward achieving carbon neutrality. When consolidating buildings for the painting, assembly, and inspection processes, we concentrated heat sources on the upper floor to support energy management by minimizing heat input to the lower floor (the work area), and created a compact plant by reducing the number of processes by approximately 15% compared to the previous plant through traverse movement of vehicles, shortened painting booth lengths, and other measures. In addition, the plant adopted air conditioning recycling in dry booths of the painting process, a new technology, and installed solar power (renewable energy) generation facilities, slashing CO2 emissions by 42% (compared to 2013) by the time the plant is in full operation in 2022. The second production line at the Karawang Vehicle Plant, which started operation in 2024, reduced CO2 emissions by 30% compared to Indonesia’s Sunter Vehicle Plant.
 A panoramic view of the Kyoto (Oyamazaki) Plant.
A panoramic view of the Kyoto (Oyamazaki) Plant.
Daihatsu upgraded the plant to serve as a model next-generation plant for the Group
Specific Initiatives for Achieving Carbon Neutrality in Production
Extensive Energy Saving by Pursuing SSC (simple, slim, and compact)
In accordance with Daihatsu’s fundamental SSC (simple, slim, and compact) concept we are taking action to eliminate waste and steadily save energy at all production sites. We have made electricity consumption at plants visible in real time, and all employees are working to eliminate waste and make improvements in energy usage.
Development and Incorporation of Innovative Technologies
Daihatsu is also actively adopting innovative energy-saving technologies that will lead to reductions in CO2. One such example is the introduction of air conditioning recycling in dry booths of the painting process at the Kyoto (Oyamazaki) Plant. The new technologies established at production sites have been expanded to the Daihatsu plants both domestically and internationally, and we also have a policy of collaborating with the Toyota Group and developing new technologies unique to Daihatsu.
 Deploying innovative technologies—Dry booths for painting processes
Deploying innovative technologies—Dry booths for painting processes
Utilization of Renewable Energy
Daihatsu has already installed solar power generation facilities at multiple plants and business sites and is promoting the use of renewable energy, and we will continue to expand the use of solar power generation throughout the Daihatsu Group in the future. We are also bolstering biogas-related initiatives.
 ADM solar power (5.6 megawatts)
ADM solar power (5.6 megawatts)